2. what are the conditions required for two matrices to be added or subtracted? *
Linear Algebra for Machine Learning: An Introduction
If yous've started looking into behind the scenes of popular auto learning algorithms, y'all might have come up across the term "linear algebra".
The term seems scary, but it isn't really so. Many of the machine learning algorithms rely on linear algebra because it provides the ability to "vectorize" them, making them computationally fast and efficient.
Linear algebra is a vast branch of Mathematics, and not all of its knowledge is required in understanding and building machine learning algorithms, then our focus will be on the basic topics related to car learning.
This article covers the fundamentals of linear algebra required for machine learning, including:
- Vectors and Matrices
- Matrix Operations (Multiplication, Addition, and Subtraction)
- Vector Operations (Addition, Subtraction, and Dot Product)
NumPy implementations for each of the operations are as well included at the finish of each topic.
Matrices
A matrix is a rectangular array of numbers arranged in rows and columns. In other words, a matrix is a 2-dimensional array comprising of numbers.
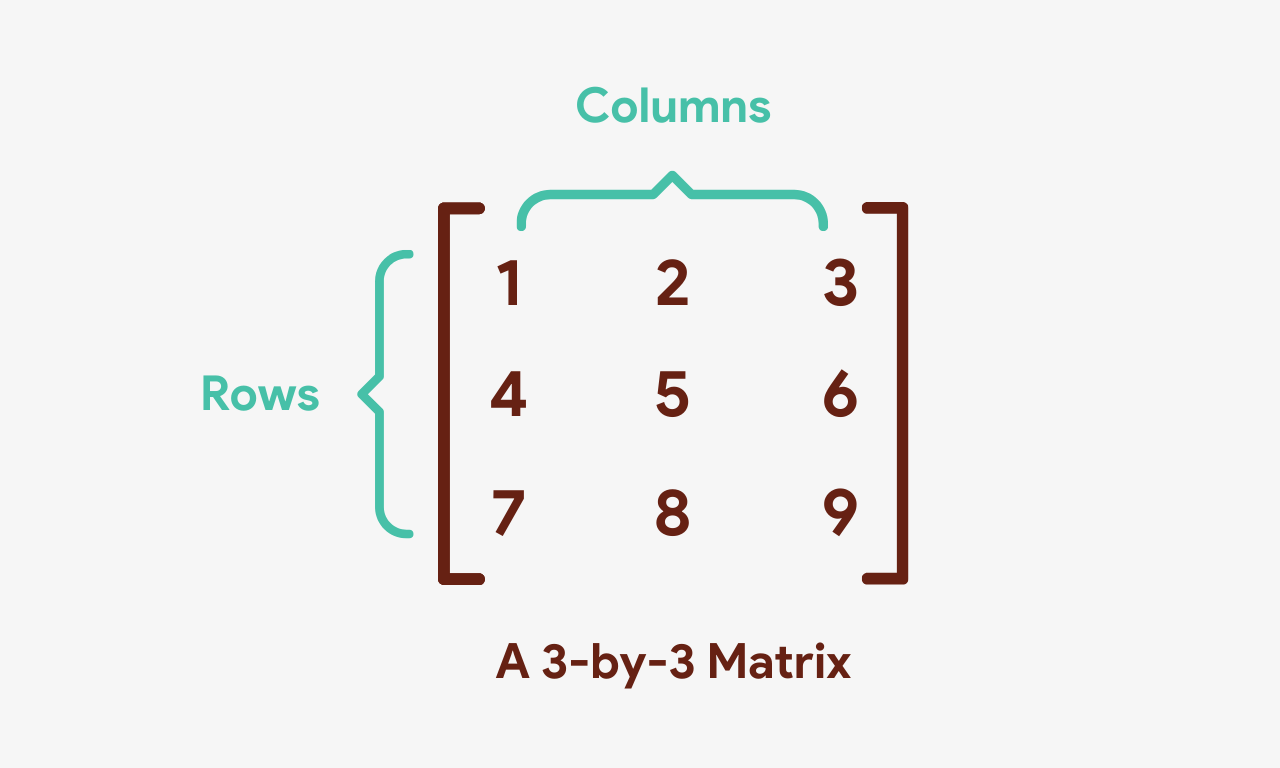
The dimensions of a matrix are denoted past m ✕ n , where thousand is the number of rows and n is the number of columns it has. The matrix shown in the above prototype is a three ✕ three matrix since information technology has three rows and 3 columns.
Python, past default, doesn't come with arrays. Lists are great, but they aren't very efficient when performing millions of numeric options. To solve this problem, we apply some sort of numerical computing library, which supports arrays and fast numeric computations. NumPy is one of them and it has several other benefits apart from that.
This is how nosotros can create a 3x3 matrix using NumPy:

Row and Cavalcade Matrices
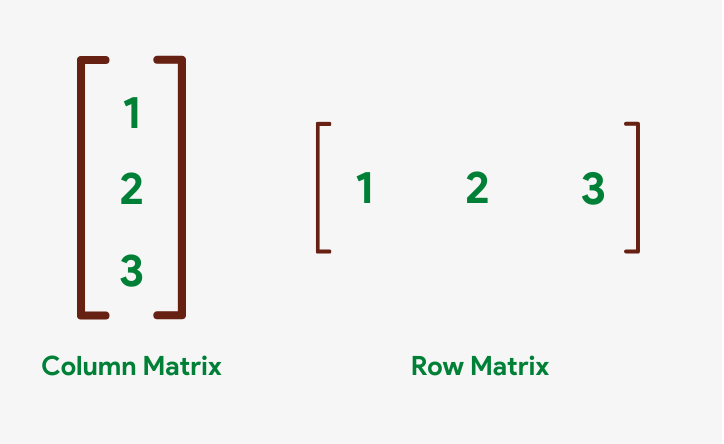
Based on the arrangement of rows and columns, matrices are divided into several types. 2 of them are row and column matrices.
A matrix having merely one column is called a column matrix while a matrix having merely one row is called a row matrix.
Operations on Matrices
Matrices support all of the bones arithmetic operations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and partitioning.
Improver
Adding two matrices is very unproblematic. The corresponding elements of the matrices are added together to class a new matrix. The resulting matrix also has the same number of rows and columns every bit the two matrices to be added.
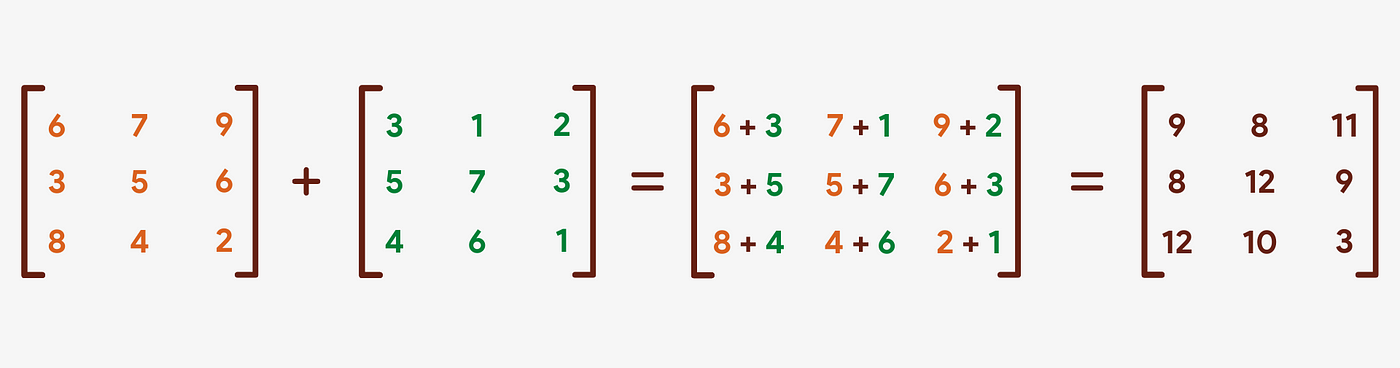
Note that both of the matrices should take the aforementioned number of rows and columns, otherwise the result will be undefined.
Subtraction
Subtracting two matrices is merely equally simple as the add-on. The corresponding terms of the two matrices are subtracted to form a new result matrix. Just like in addition, both of the matrices should have the aforementioned dimensions.
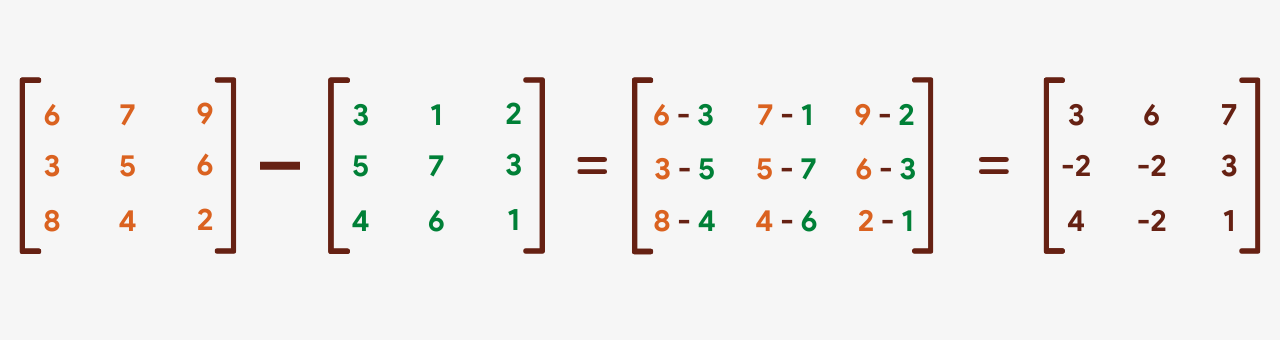
Scalar Multiplication
Multiplying a matrix past a number is chosen scalar multiplication. This kind of multiplication is very piece of cake, as nosotros just have to multiply each of the elements of the matrix by that number.
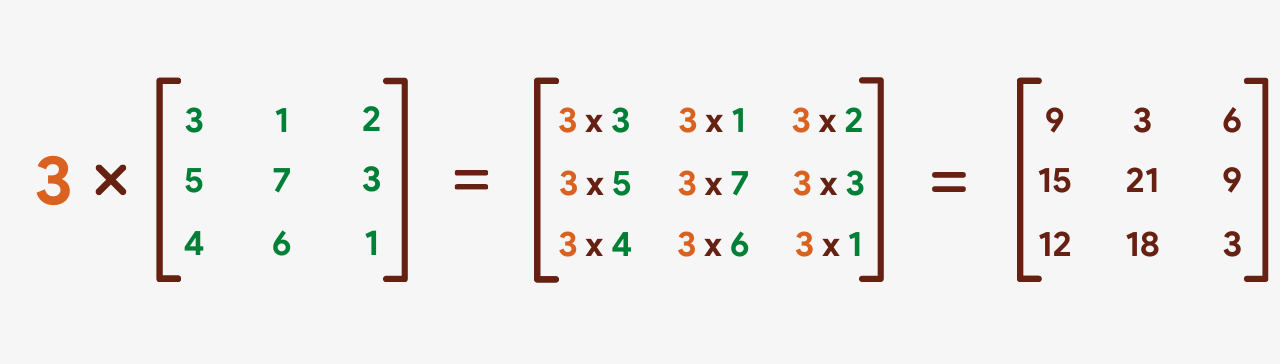
Scalar Division
Dividing a matrix by a scalar is likewise very simple. Each of the elements in the matrix is divided by the number to form a new result matrix.
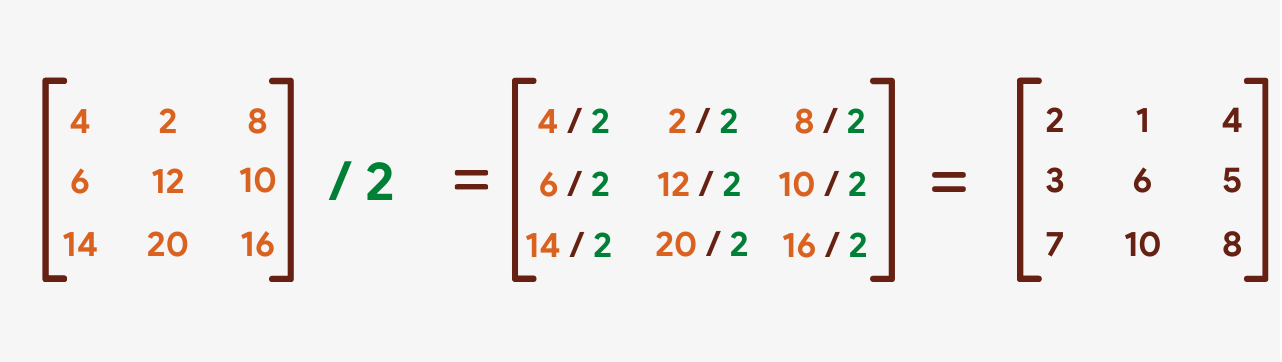
Matrix-Matrix Multiplication
Multiplying a matrix past another matrix is called "matrix multiplication" or "cross product". Matrix multiplication is very easy, but a fleck tricky for beginners to understand.
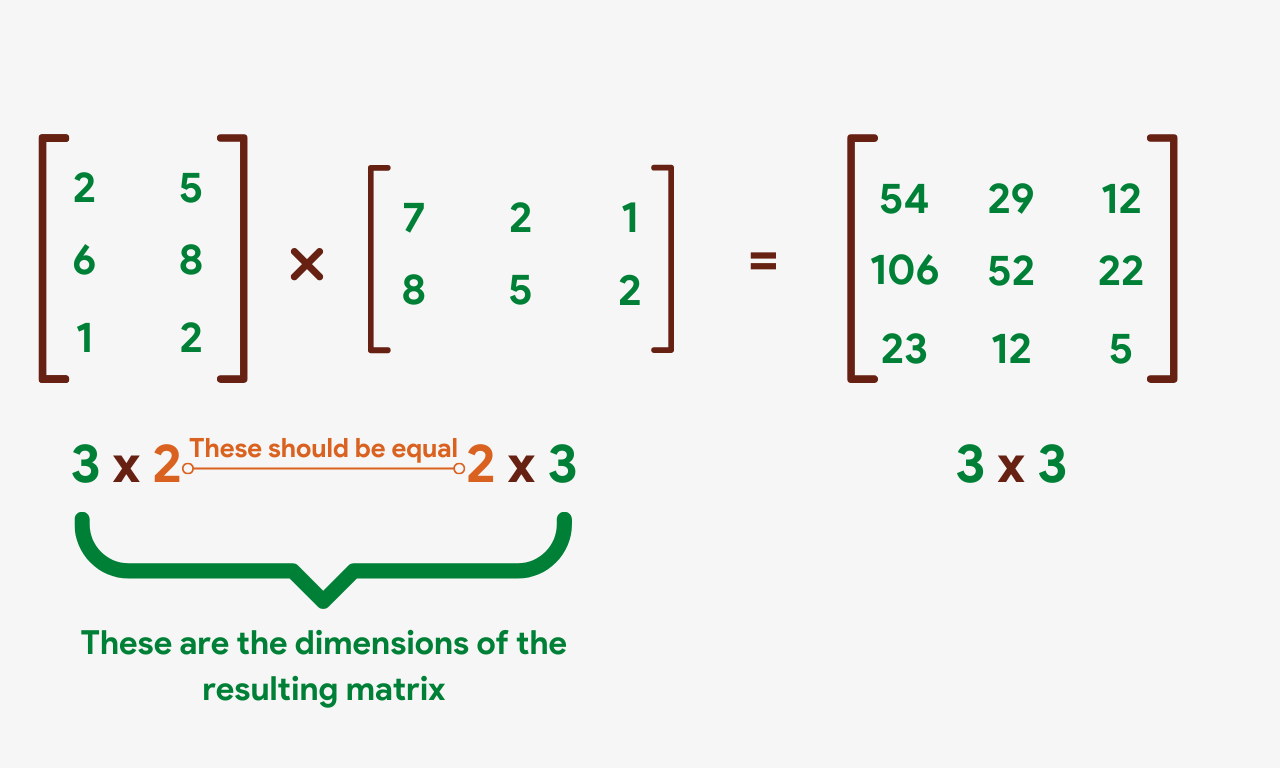
Allow'southward accept ii 3ten3 matrices, A and B, as shown below:
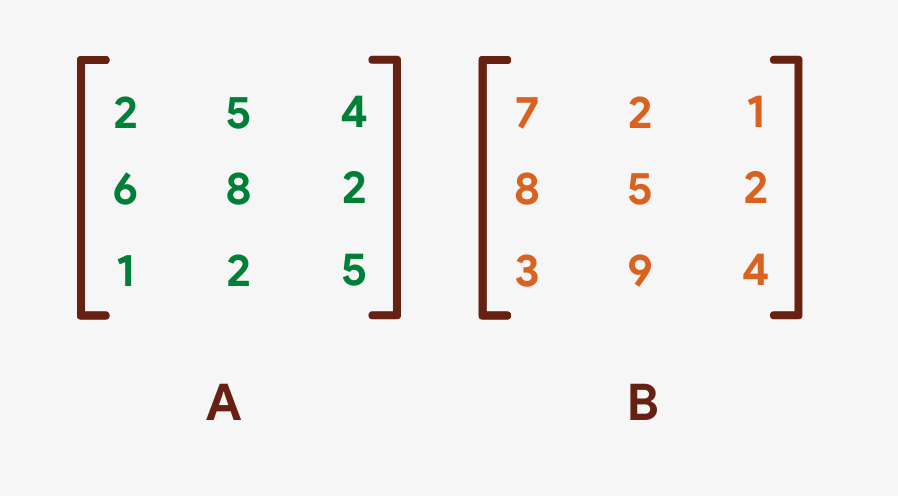
To brainstorm with, we'll multiply each of the numbers in the first row of A past the corresponding numbers in the get-go column of B. The sum will then be put in the result matrix every bit shown below:
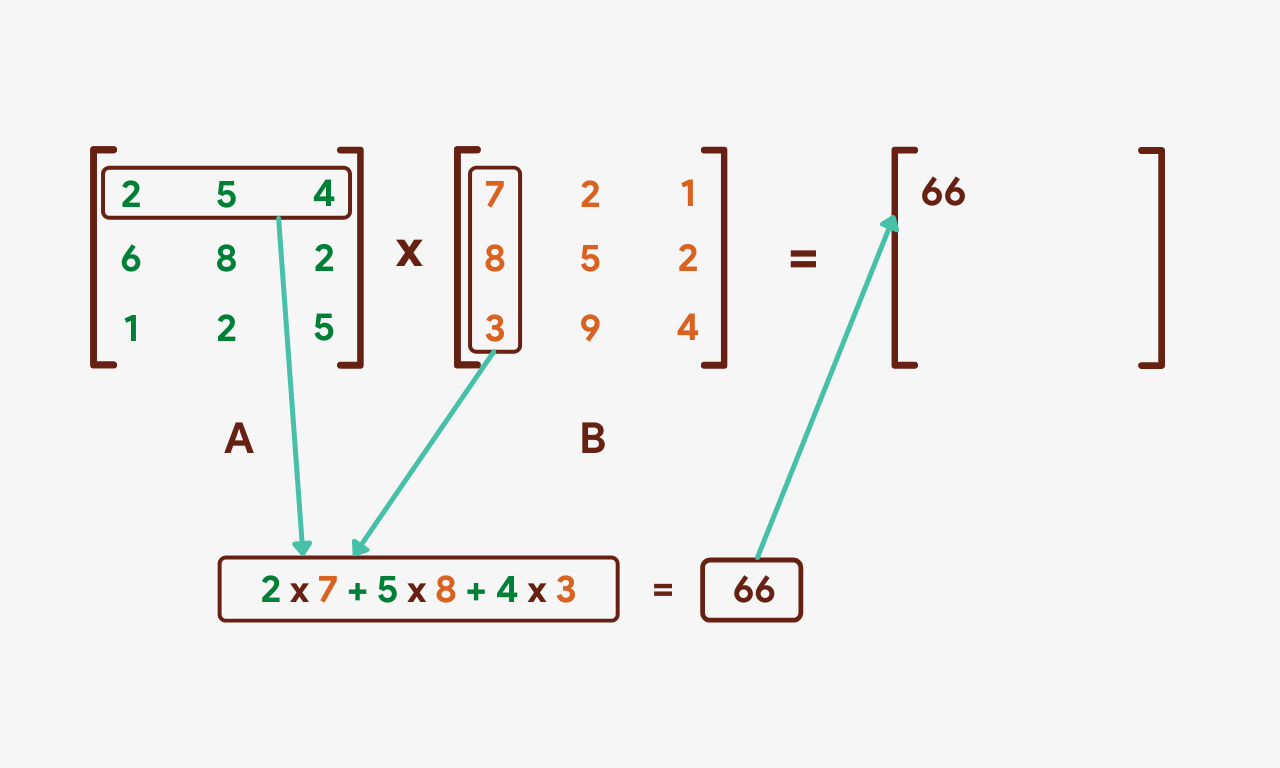
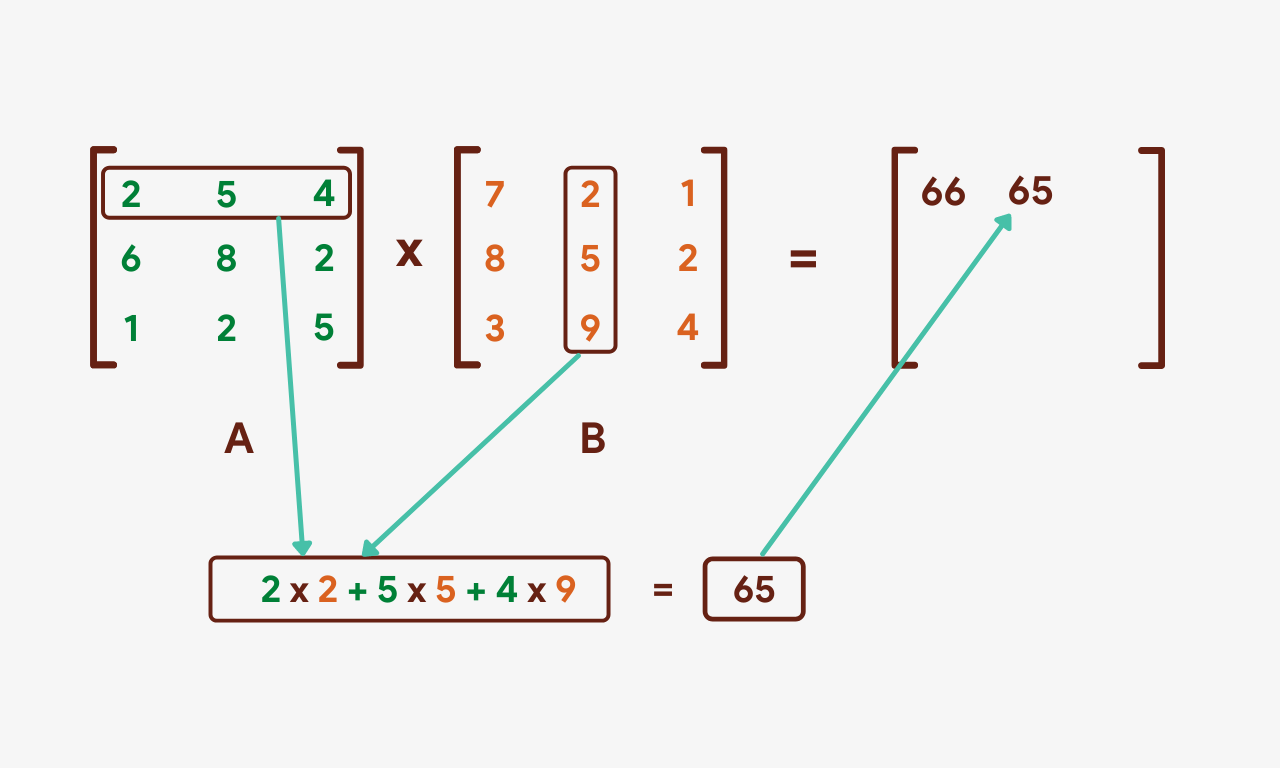
Nosotros'll once again take the product of the first row of matrix A just this fourth dimension with the second column of matrix B.
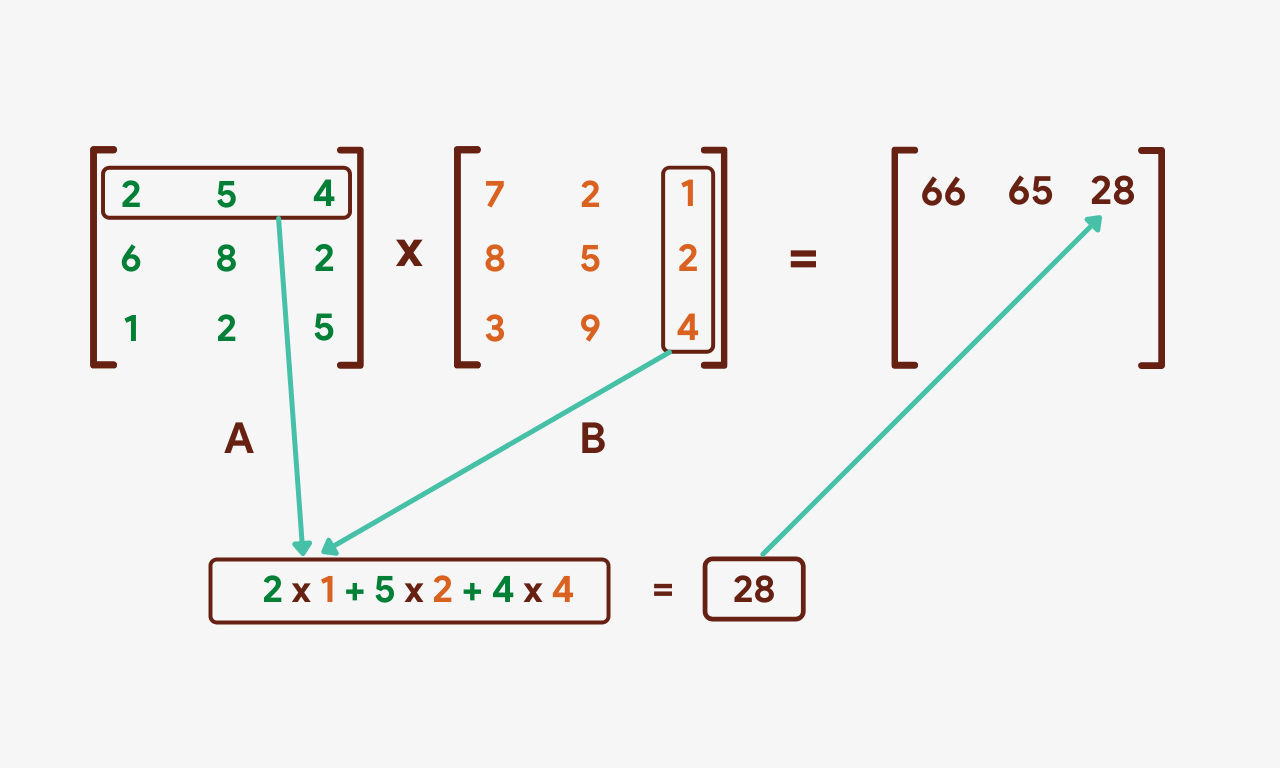
The same process will be repeated for the 3rd cavalcade of matrix B.
Let's repeat this process for the 2nd and 3rd rows of matrix A.
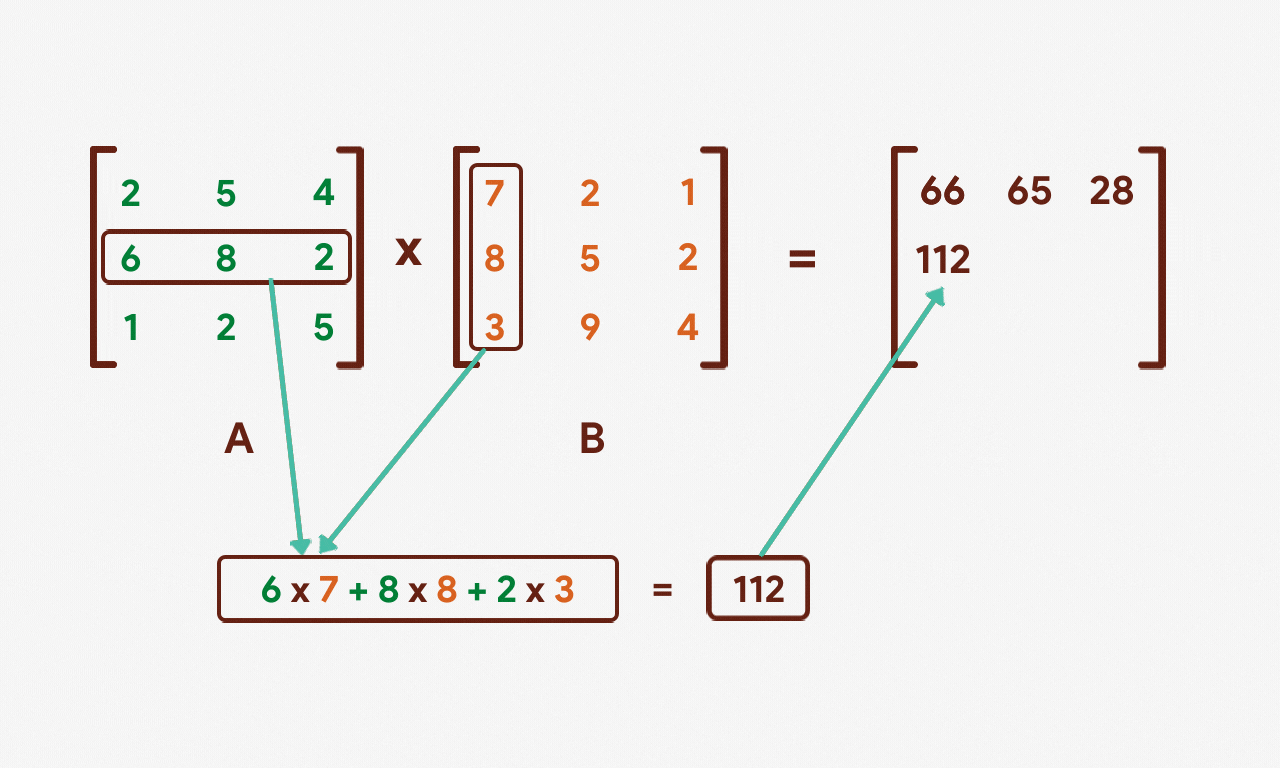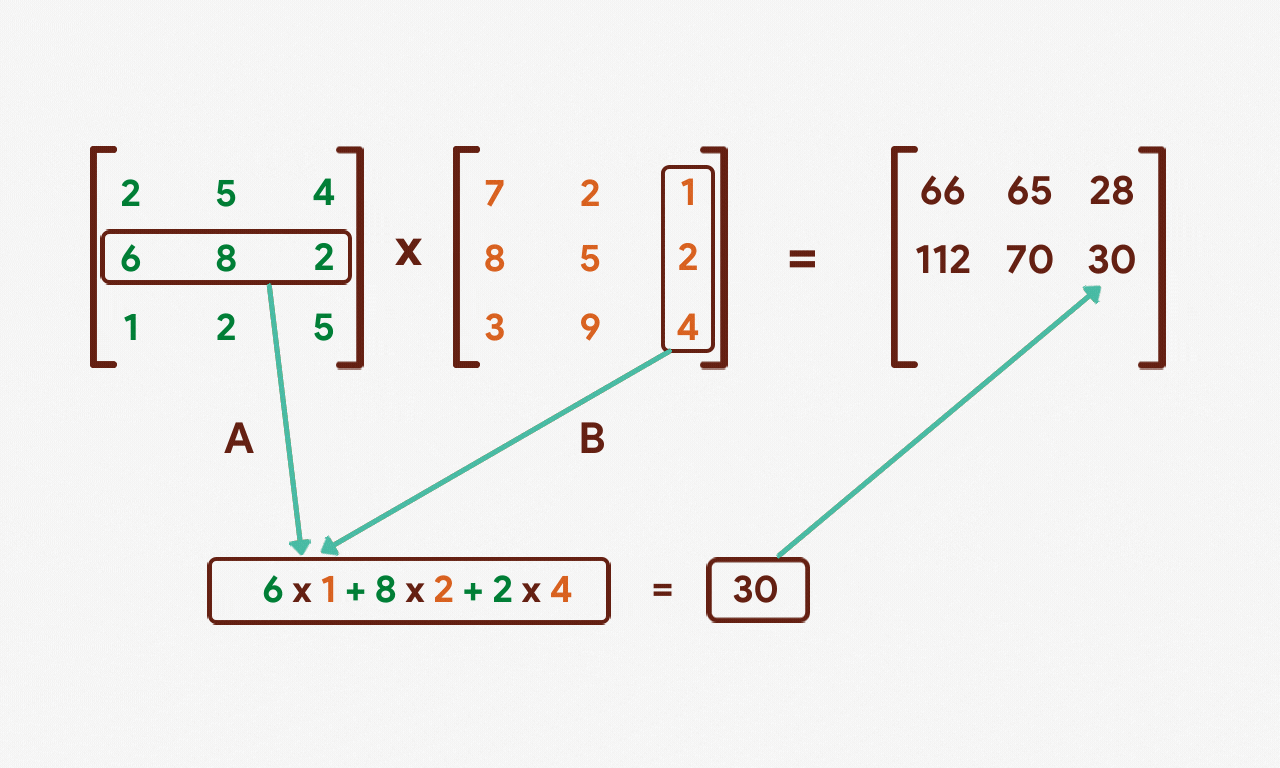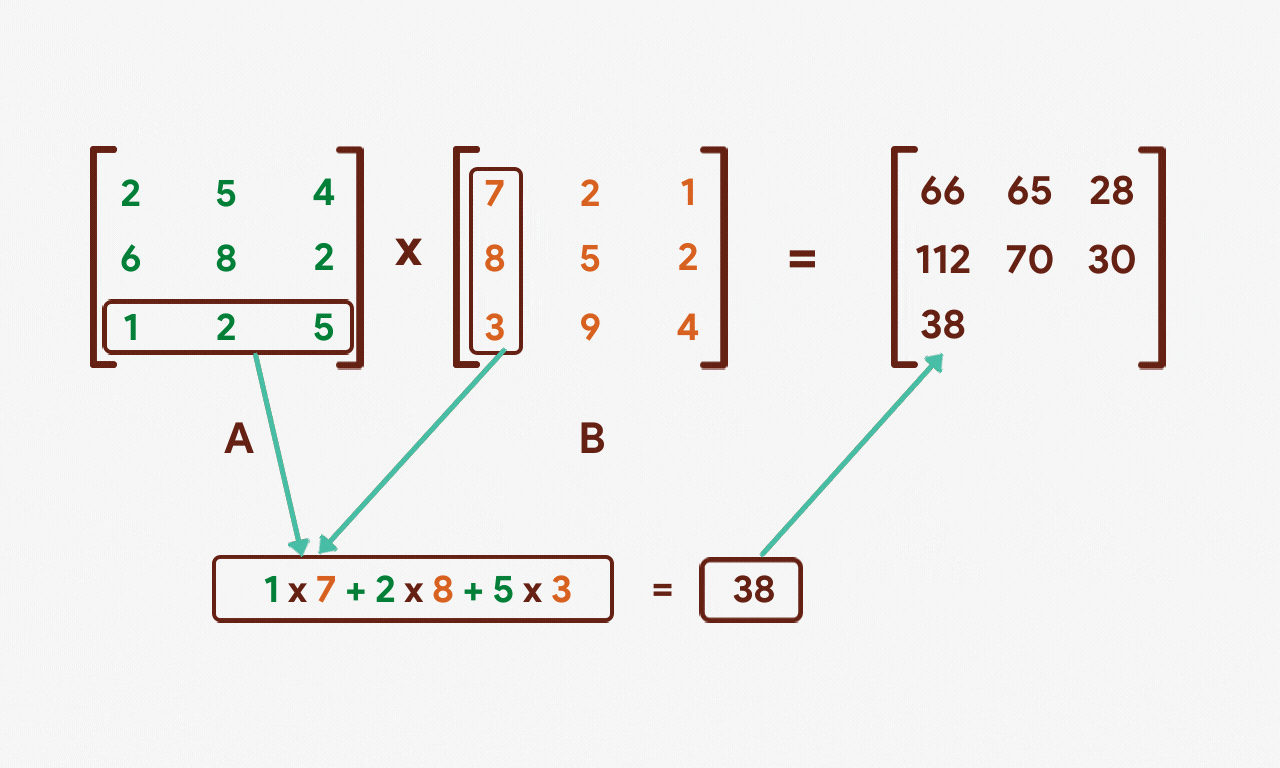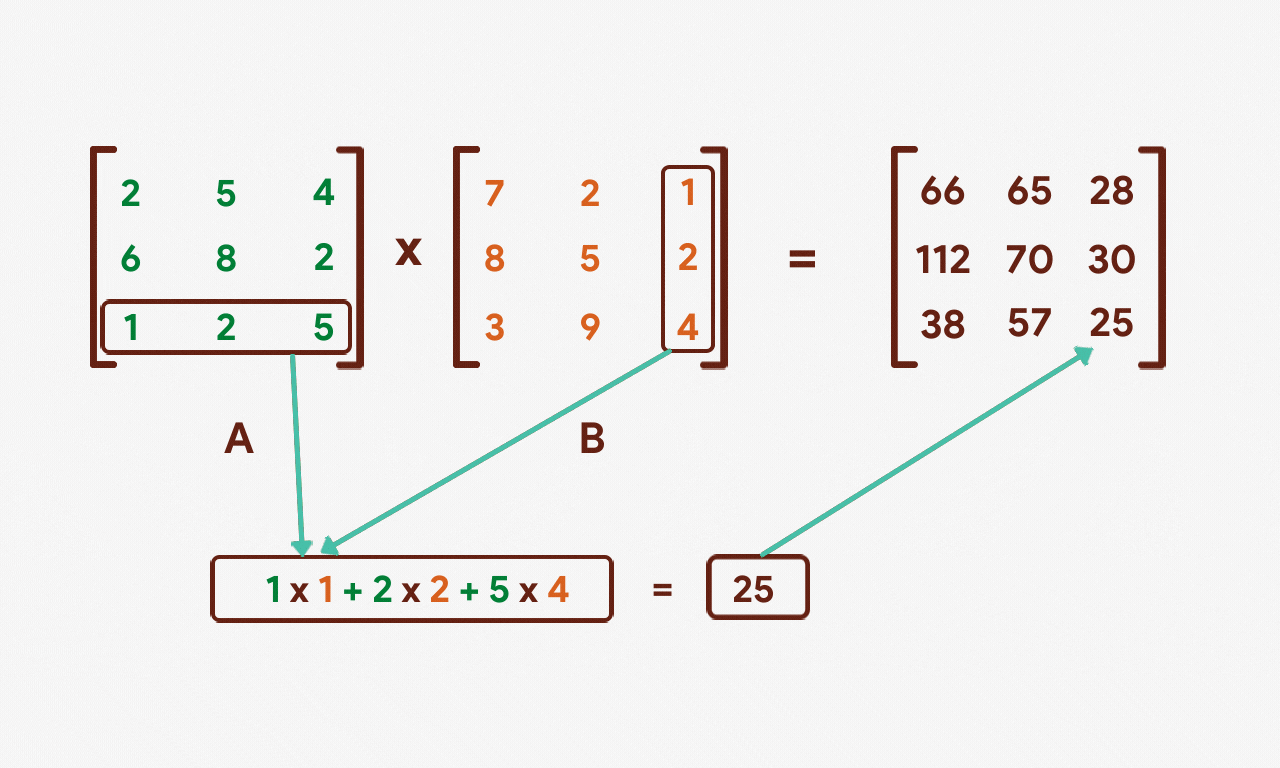
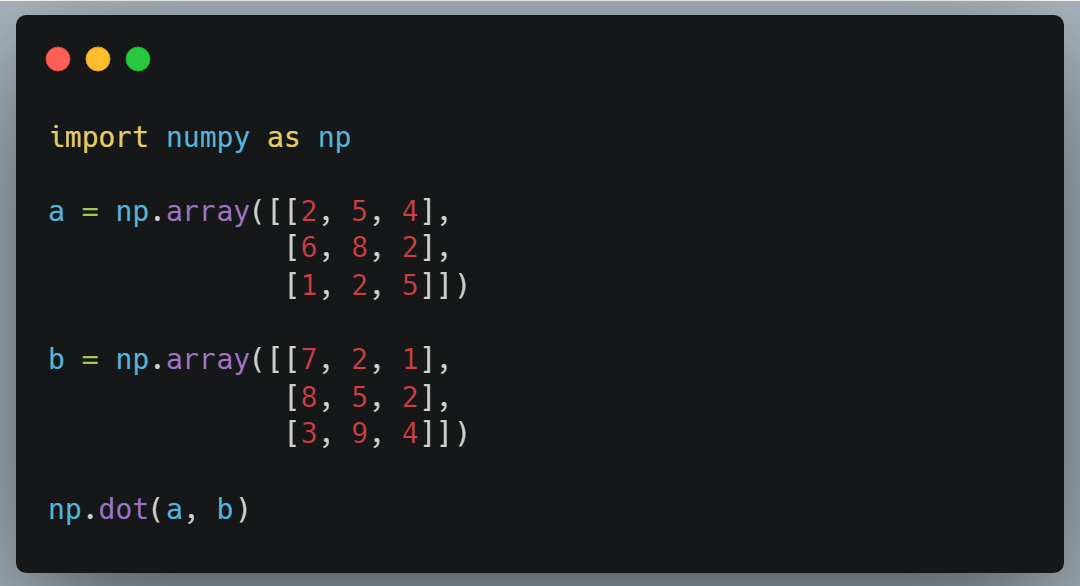
Using NumPy, we can multiply two matrices with each other by using the numpy.dot() function.
There are a few things worth noting about matrix multiplication:
- When multiplying 2 matrices, the number of columns in the beginning matrix must exist the same as the number of rows in the 2d matrix. In other words, the inner dimensions of the ii matrices must be the same.
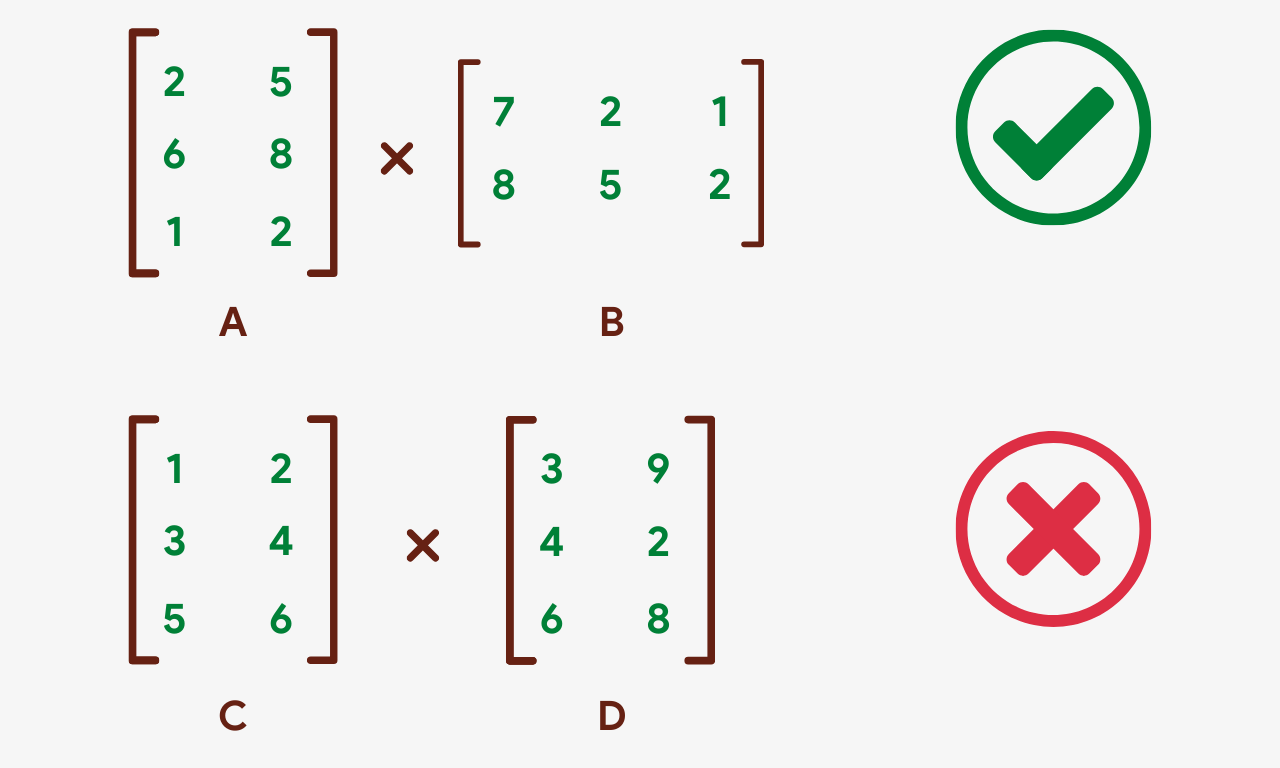
In the higher up image, the matrices A and B tin be multiplied since A has 2 columns and B has 2 rows. The matrices C and D can't exist multiplied because C has simply 2 columns while D has iii rows.
- The dimensions of the resulting matrix will be equal to the outer dimensions of the 2 matrices to exist multiplied, i.e. the resulting matrix will accept the number of rows of the first matrix and the number of columns of the 2d matrix.
- The production of two matrices is NOT commutative. It means that A multiplied past B is non equal to B multiplied past A.
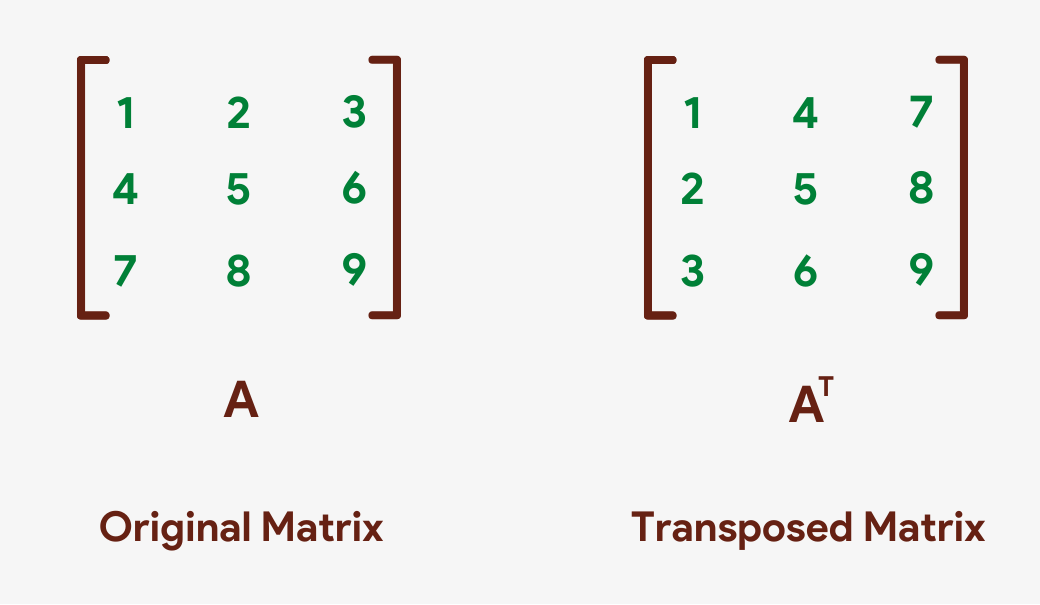
Transpose of a Matrix
Transposing a matrix means swapping its rows and columns with each other, i.e. changing its rows into columns and columns into rows. The transpose of a matrix is often denoted by a capital T in superscript. For case, Aᵀ will denote the transpose of matrix A.
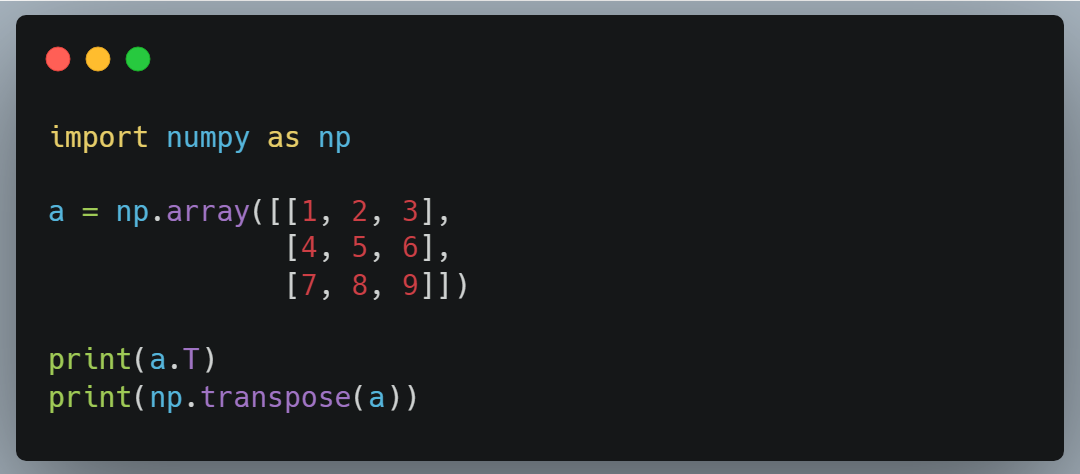
In NumPy, a matrix (array) can exist transposed either using the array'southward own .T method or using the numpy.transpose() role.
Vectors
In linear algebra, a vector is a quantity having a management along with its magnitude. However, this definition is very much Physics-based. Allow's define it in our own terms.
A vector can be thought of as an m x 1 matrix or a column matrix. The number of rows in a vector tells the dimension of a vector. For instance, a vector having 3 rows will be called a iii-dimensional vector.

Unlike matrices, vectors are created as 1-d arrays instead of 2-d arrays when using NumPy.

Dot Production of Vectors
When two vectors are multiplied, the issue is a numeric value and is called their dot production.
The dot production of two vectors is calculated past multiplying their corresponding elements by each other and and so summing them all.
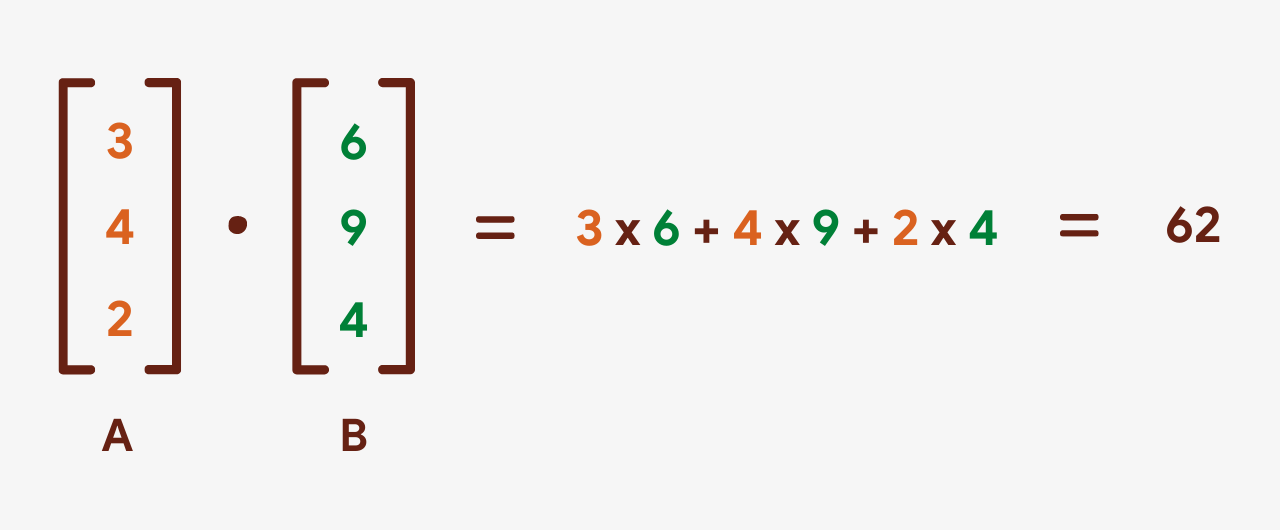
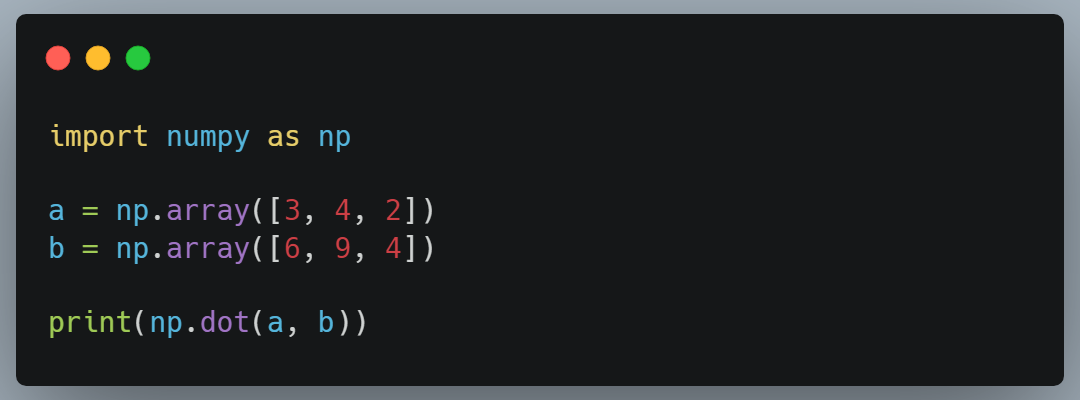
This is how the dot production of 2 vectors can be calculated using NumPy:
The dimensions of the two vectors should be the same when computing their dot product.
Unlike matrix multiplication, the dot product of two vectors is commutative, pregnant that A • B = B • A.
Determination
Using linear algebra makes motorcar learning computation very fast by introducing vectorization. NumPy is one of the libraries used to vectorize machine learning algorithms. This article introduced you to some basics of linear algebra for car learning, such every bit matrices, vectors, matrix add-on, multiplication, and the dot production of matrices. The purpose of this guide was to make you familiar with the basics of linear algebra and then that you don't feel missed out when looking at the Math behind various machine learning algorithms.
Source: https://medium.com/artificialis/linear-algebra-for-machine-learning-an-introduction-9111777c0b9a
0 Response to "2. what are the conditions required for two matrices to be added or subtracted? *"
Enviar um comentário